Fleshy fruits
In fleshy fruits (fleshy simple fruits), one or more of the pericarp layers remains fleshy at maturity.
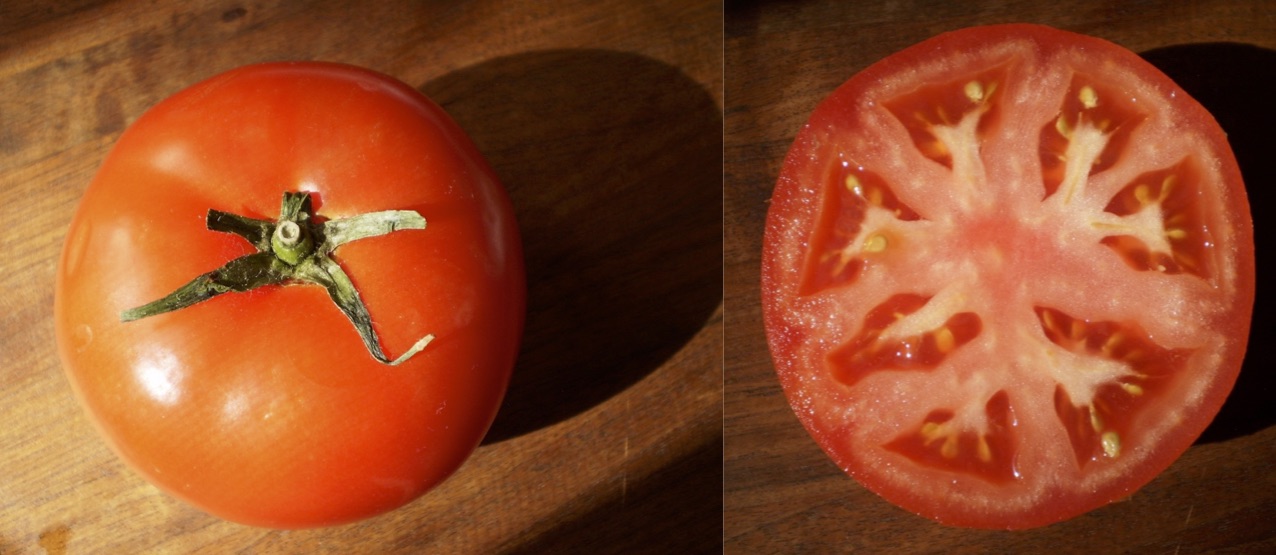
In a berry, all layers of the fruit wall are fleshy at maturity.

In a drupe, the exocarp and (especially) the mesocarp are fleshy, but the endocarp is hard (stony). These are sometimes called stone fruits. The "pits" in these fruits are not simply the seed; they are the stony endocarp that encloses the seed.
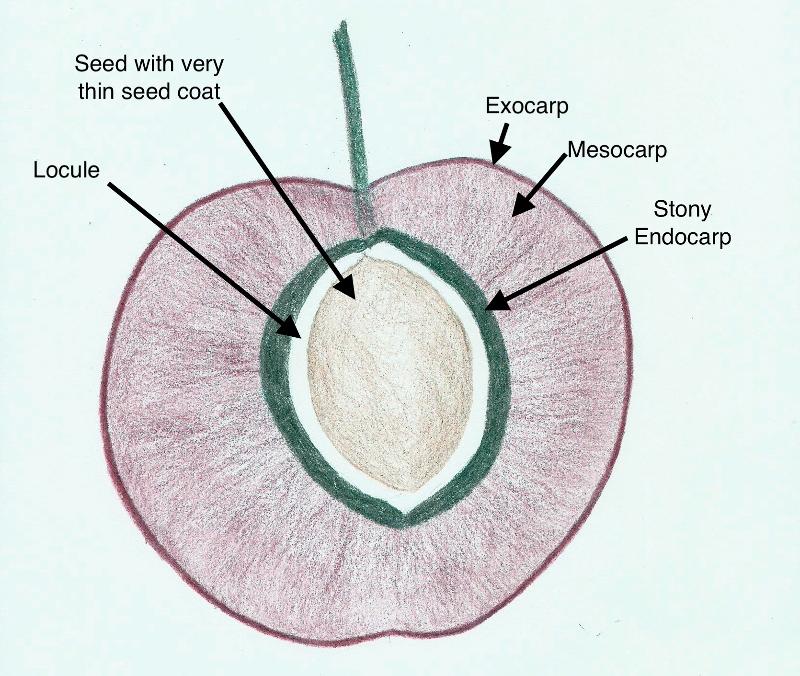
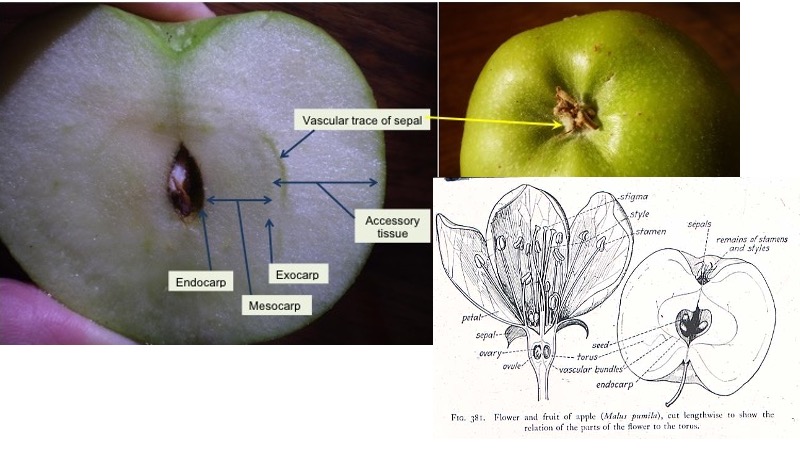
In a pome, the exocarp and mesocarp are fleshy, but most of the fruit's flesh is composed of other tissue (receptacle/hypanthium) that is fused to the outside of the ovary. This is not a common fruit type, but we do find it in the rose family (the Rosaceae): apples and pears are examples of pomes.
Other fleshy fruits, which you will not need to know for this class, include the pepo (a fleshy fruit from an inferior ovary in the Cucurbitaceae) and the hesperidium (a citrus fruit).