Leaf margins and surface features
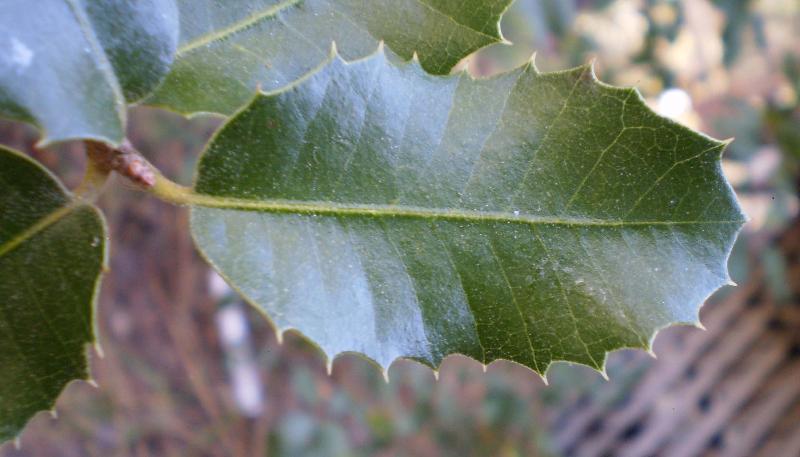
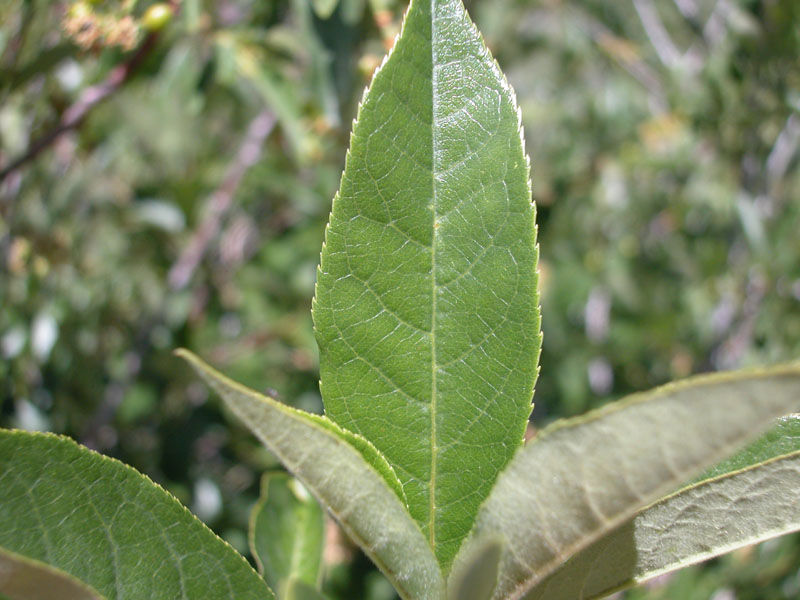
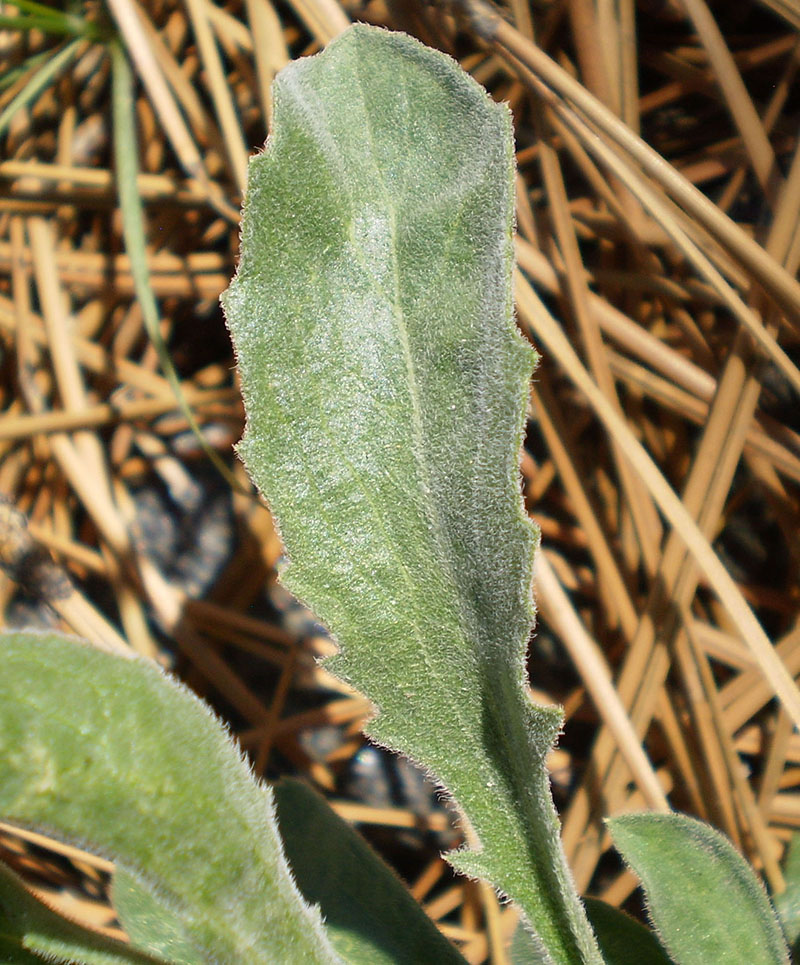
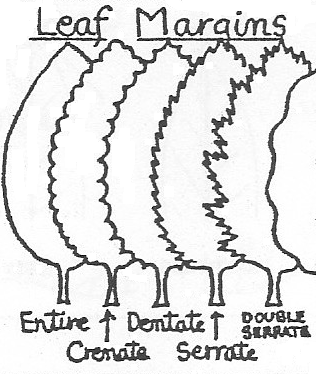
Leaf margins
The leaf margin (or leaf edge) may be smooth or variously toothed or scalloped.
- A smooth magin (not toothed in any way) is called an entire margin.
- A toothed margin is sometimes called "dentate" (meaning "toothed")
- If the teeth slant toward the tip of the leaf, however, the margin is called serrate.
- Sometime large serrations have smaller serrations on them. These margins are called doubly serrate.
- A crenate margin has rounded teeth with acute sinuses between the teeth. (It is scalloped.)
Leaf hairs may cover the surface of leaves (below), but if hairs are on the margin, rather than the surface, the leaf is called ciliate.
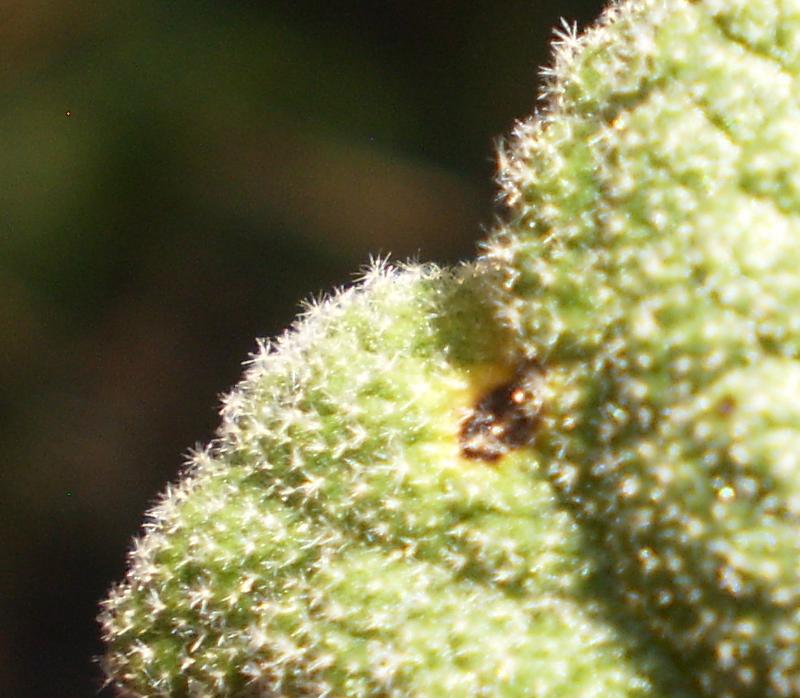
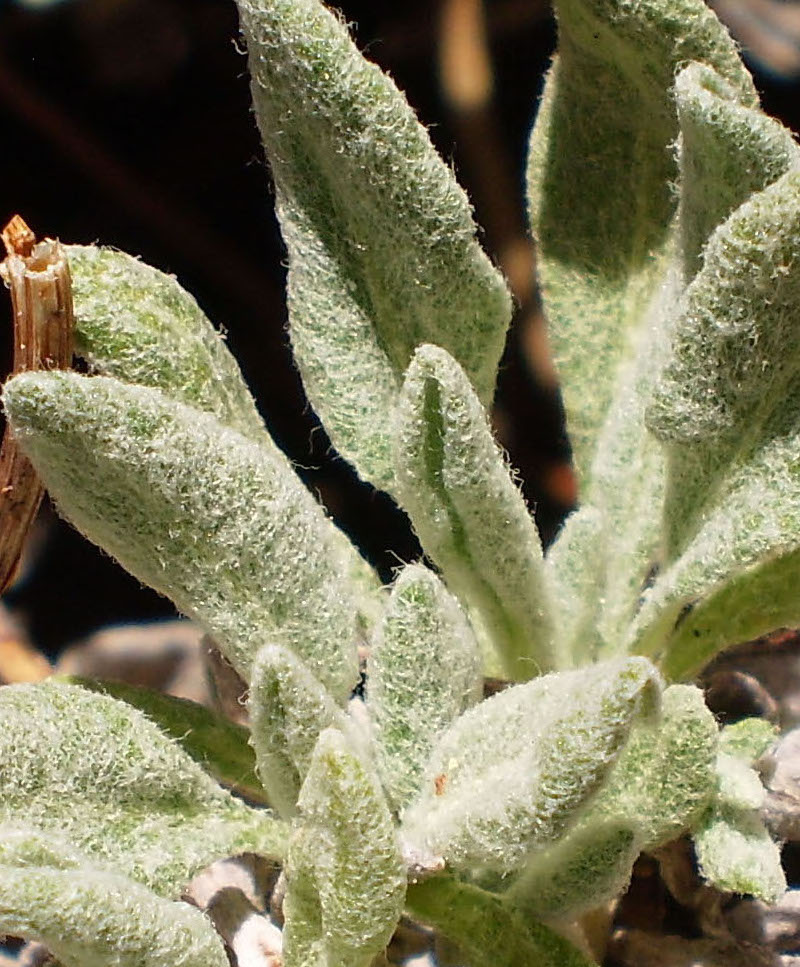
Leaf surface features
Leaf surfaces may have various types of hairs, bumps, or color and sheen.
Glabrous surfaces have no hairs.
Glaucus surfaces are glabrous, but the cuticle structure gives the surface a white, milky look.

Hairy surfaces may be described in different ways, depending on the structure of the hairs.
Hairs may be simple (unbranched), branched or forked, or stellate (with many branches radiating from a central point).
Hairy surfaces may be described as...
- puberulent, if the the hairs are short, fine, and soft
- canescent, if the hairs are dense, fine, and generally grayish white
- villous, if the hairs are long, soft, and wavy
- tomentose, if the hairs are wooly and matted
- strigose, if the hairs are straight, stiff, appressed, and pointing the same direction
- scabrous, if the surface is rough to the touch. This is usually caused by very short, stiff hairs or sharp bumps.
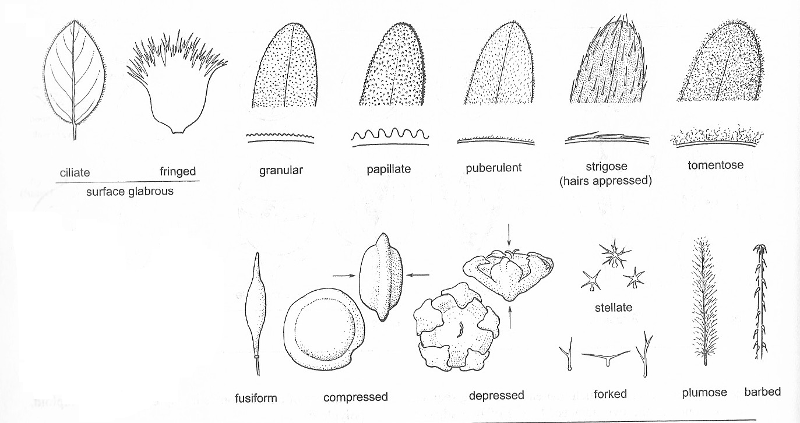
Some surfaces may have glandular hairs or sunken glands.

Check your understanding:






