Deserts and Desert Environments
Deserts occur in areas with low precipitation (lower than is found in mediterranean climate). Temperature can be hot or cold, precipitation can come as snow or rain, and seasonal patterns of precipitation can vary among deserts.
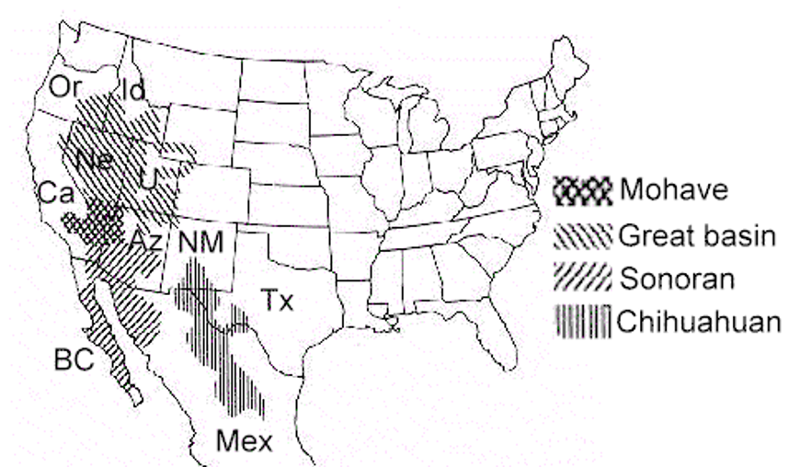
California's transmontane region falls into three different deserts: the Great Basin Desert, the Mojave Desert, and the Sonoran Desert. These deserts differ in temperature and/or precipitation patterns. They also differ in the plant species that dominate them.
The Mojave Desert
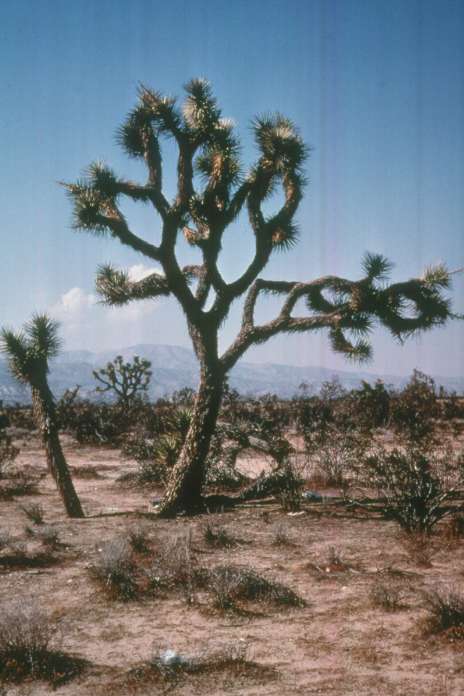

The Mojave Desert is the driest desert of California's three deserts. It has dry summers and extreme temperature swings. It is the desert that exists across the mountains to the east of CSUSB.
Yucca brevifolia (Joshua tree) is generally considered an indicator species of the Mojave Desert.
The Sonoran Desert
The Sonoran Desert lies to the south of the Mojave Desert. It is hotter, on average, than the Mojave Desert, but it is not as dry during the summer. It has a bimodal pattern of rainfall with winter rains and summer thunderstorms.
The giant saguaro cactus (Carnegiea gigantea) is endemic to the Sonoran Desert .

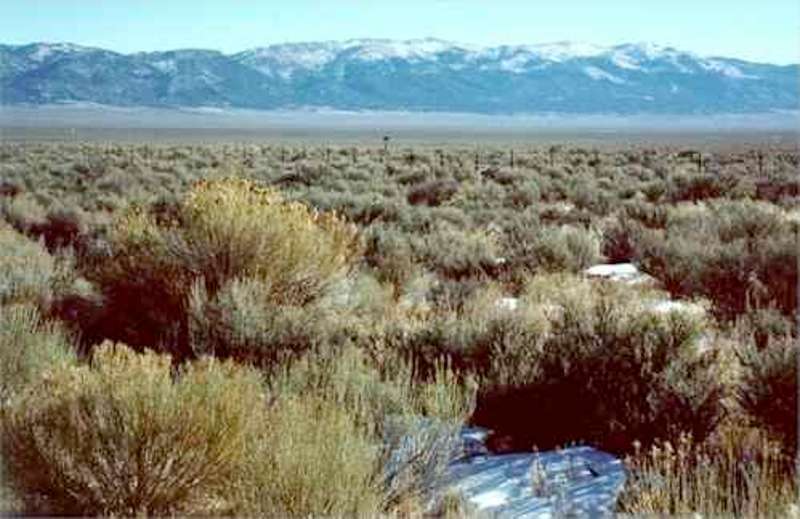
Great Basin Desert
The Great Basin Desert is the coldest desert in California. It exists primarily in Nevada, western Utah, and soutnern Idaho, but it covers small bits of southeastern Oregon and eastern California.
Precipitation in the Great Basin Desert comes primarily in the winter and as snowfall.
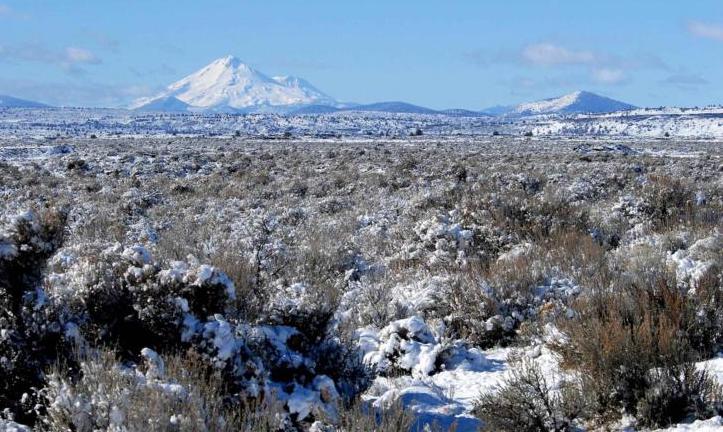

The dominant plant species of the Great Basin Desert is big sagebrush (also known as Great Basin sagebrush), Artemisia tridentata.
